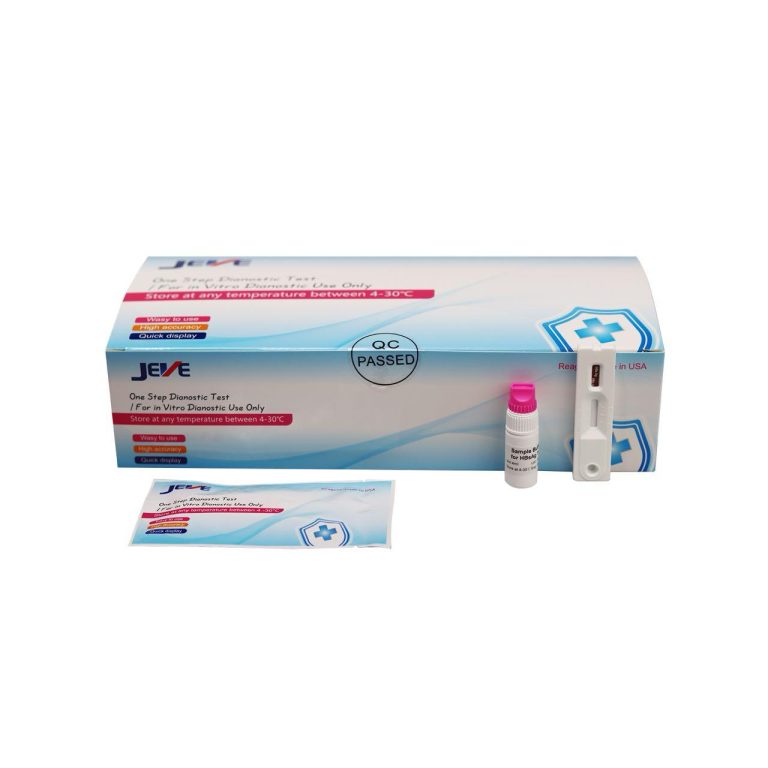
HBsAg Hepatities B Surface antigen Test Cassette
The HBsAg Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Test Cassette is a rapid diagnostic test used to detect the presence of Hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) in human blood, serum, or plasma. Here’s a breakdown of its key features and information:
Purpose:
- Aids in screening for current Hepatitis B infection by detecting HBsAg, a protein produced by the Hepatitis B virus (HBV).
- Not a confirmatory test for chronic HBV infection or past exposure.
Function:
- Employs a lateral flow immunoassay method. When a blood sample is applied, it migrates across a membrane containing antibodies specific to HBsAg.
- If HBsAg is present, a colored line appears in the “test” region, indicating a reactive or positive result.
- A control line should always be visible to validate the test’s functionality.
Benefits:
- Rapid Results: Provides results within a short timeframe, typically 10-30 minutes.
- Easy to Use: Generally requires a small blood sample and can be performed in various settings, including clinics or point-of-care locations.
- Relatively Non-invasive: Uses a finger prick for blood collection, minimizing discomfort.
Limitations:
- Qualitative Test: Provides a positive or negative result, but doesn’t distinguish between acute or chronic infection or past exposure with immunity.
- Accuracy: May not be as accurate in the early stages of infection when HBsAg levels haven’t peaked.
- Confirmatory Testing Required: A positive result on this rapid test needs to be confirmed by more specific tests like an anti-HBc antibody test (detects past or current infection) and an anti-HBs antibody test (detects immunity).
Applications:
- People with risk factors for Hepatitis B infection, such as individuals with a history of intravenous drug use, unprotected sexual contact, or exposure to contaminated needles.
- Individuals experiencing symptoms suggestive of hepatitis, such as fatigue, nausea, vomiting, or jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes).
- Pregnant women to prevent mother-to-child transmission.
- Routine screening for healthcare workers or others at increased risk of exposure.
Important Considerations:
- A positive test result should be followed by confirmatory testing with a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate course of action.
- A negative test result may not completely rule out Hepatitis B infection, especially in the very early stages.
- Always consult a doctor to interpret the test results and discuss any questions or concerns you may have about Hepatitis B.
















Reviews
There are no reviews yet.